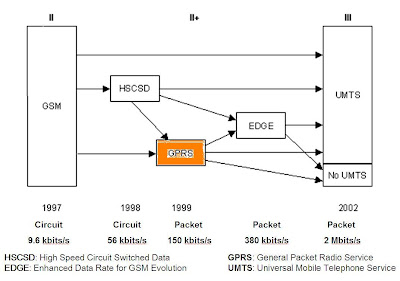
GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) is a packet based upgrade to the GSM networks. It allows GSM networks to be truly compatible with the Internet. GPRS uses a packet-mode technique to transfer bursty traffic in an efficient manner. It promises data rates from 56 up to 114 Kbps and continuous connection to the Internet for mobile phone and computer users. Along the evolution path of the GSM network towards 3G and beyond, GPRS is refered as a 2.5G technology.
1. GPRS Network Architecture

2. GPRS Network Entities
2.1 MS
GPRS enabled MS.
2.2 BTS
Same as the GSM BTS.
2.3 BSC
The GSM BSC enhanced with the Packet Control Unit (PCU) to differentiates whether data is to be routed to the packet switched or circuit switched networks.
The PCU or Packet Control Unit is a hardware router that is added to the BSC. It differentiates data destined for the standard GSM network (circuit switched data) and data destined for the GPRS network (Packet Switched Data). The PCU itself may be a separate physical entity, or more often these days it is incorporated into the base station controller, BSC, thereby saving additional hardware costs.
2.4 SGSN
The SGSN or Serving GPRS Support Node element of the GPRS network provides a number of takes focussed on the IP elements of the overall system. It provides a variety of services to the mobiles:
• Packet routing and transfer
• Mobility management
• Attach/detach
• Logical link management
• Authentication
• Charging data
There is a location register within the SGSN and this stores location information (e.g., current cell, current VLR). It also stores the user profiles (e.g., IMSI, packet addresses used) for all the GPRS users registered with the particular SGSN.
2.5 GGSN
The GGSN, Gateway GPRS Support Node is one of the most important entities within the GPRS network architecture.
The GGSN organises the interworking between the GPRS network and external packet switched networks to which the mobiles may be connected. These may include both Internet and X.25 networks.
The GGSN can be considered to be a combination of a gateway, router and firewall as it hides the internal network to the outside. In operation, when the GGSN receives data addressed to a specific user, it checks if the user is active, then forwarding the data. In the opposite direction, packet data from the mobile is routed to the right destination network by the GGSN.
3. GPRS Interfaces and Protocols

4. GPRS Control and User Planes


5. GPRS Core Protocol -- GTP
GPRS Tunnelling Protocol (GTP) is the core protocol used in GPRS network between the SGSN and the GGSN for GPRS service control and user data delivery. It is is a group of IP-based communications protocols. GTP can be classified into separate protocol subgroups according to their usage, GTP-C, GTP-U and GTP' respectively.
GTP-C is used within the GPRS core network for signaling between the GGSN and the SGSN. GTP-C includes the control procedures that allows the SGSN to activate a session on a user's behalf (PDP context activation), to deactivate the same session, to adjust quality of service parameters, or to update a session for a subscriber who has just arrived from another SGSN.
GTP-U is used for carrying user data within the GPRS Core Network and between the Radio Access Network and the core network. The user data transported can be packets in any of IPv4, IPv6, or PPP formats.
GTP' (GTP prime) uses the same message structure as GTP-C and GTP-U, but has an independent function. It can be used for carrying charging data from the Charging Data Function (CDF) to the Charging Gateway Function (CGF).

6. GPRS User Sessions -- PDP Context
A Packet Data Protocol (PDP) context is a GPRS user session established allowing the MS and the network to exchange IP packets with QoS specifications. A PDP Context has a record of parameters, which consists of all the required information for establishing the end-to-end connection:
• PDP Type
• PDP address type
• QoS profile request (QoS parameters requested by user)
• QoS profile negotiated (QoS parameters negotiated by network)
• Authentication type (PAP or CHAP)
• DNS type (Dynamic DNS or Static DNS)
